Take this passive sentence.
Passive infinitive attic greek.
Ancient greek grammar is morphologically complex and preserves several features of proto indo european morphology.
The word is derived from late latin modus infinitivus a derivative of infinitus meaning unlimited.
Future system without contraction 36.
Future system active and middle with contraction in έω.
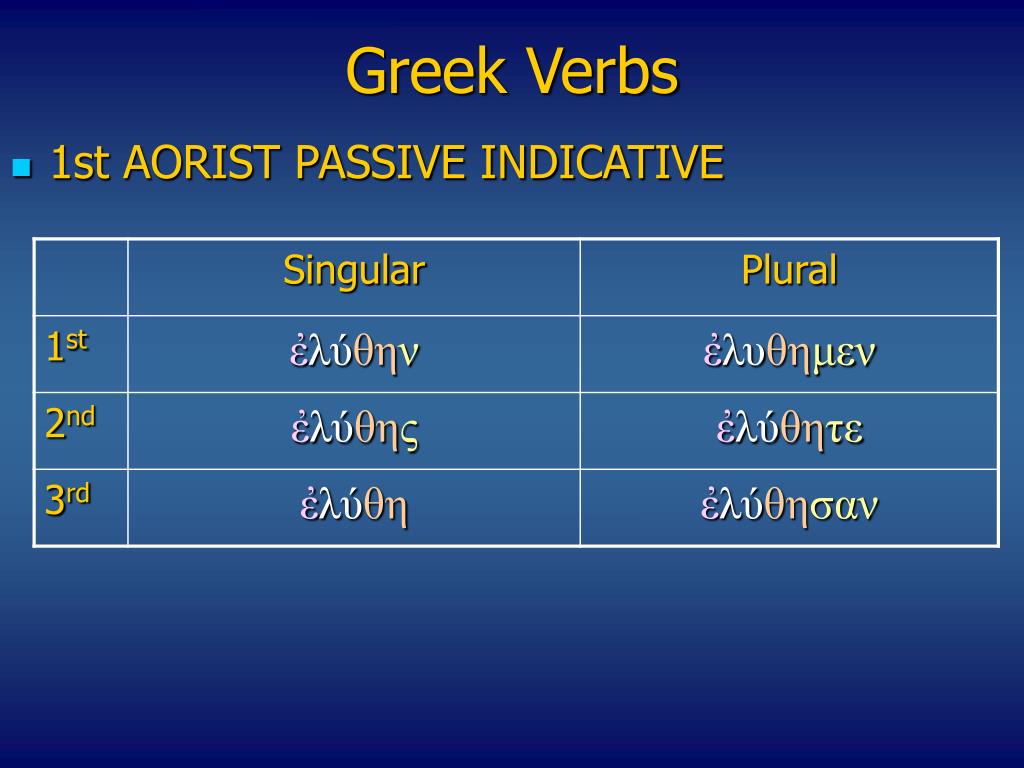
Learn the eleven forms of the infinitive active middle and passive of λύω.
A sentence constructed in a passive manner may not have a clear subject doing the action of the verb.
Infinitive mood expresses a verbal idea without indicating person and number.
In the classical language they are suppleted by the corresponding active forms of ἀποθνῄσκω apothnḗiskō however the aorist middle ἀπέκτατο apéktato is used with passive meaning in homer.
Nouns adjectives pronouns articles numerals and especially verbs are all highly inflected.
Passive versus active infinitive sentence construction.
Middle voice personal endings.
The infinitive formation of the infinitive.
Mastronarde s book introduction to attic greek.
Infinitive abbreviated inf is a linguistics term referring to certain verb forms existing in many languages most often used as non finite verbs as with many linguistic concepts there is not a single definition applicable to all languages.
Future system active with contraction in άω.
The infinitive in ancient greek goes beyond this.
Recall that there are two types of greek verbs in the present tense.
The greek verb can change in person and number.
The middle and passive differ from one another in form only in the future and aorist.
But let s back up to first show just what passive construction also called passive voice is.
A cheer was heard from the field.
Thus present active indicative shows that the action happens in the present time that the subject carries out the action and that it is a true statement.
Athematic and thematic verbs.
To love is good.
The passive forms are late.
μι verbs athematic ω verbs thematic in the active voice present tense athematic and thematic verbs use somewhat different endings to designate person and number as well as the infinitive.
The tenses occurring in the infinitive are the present future aorist perfect and future perfect.
Another complication of greek grammar is that different greek authors wrote in different dialects all of which have slightly different grammatical forms see ancient greek dialects.
The infinitive takes on a different use if an article is found in front of it.